ALERTS !
NEWS
New FDA Approved Treatment for Hyperhidrosis – SLUCare Health Watch
More than 15 million Americans suffer from excessive sweating, called hyperhidrosis and have no idea they have options. Although excessive sweating is not considered to be a life-threatening condition, it can have a profound impact on daily life, making even simple tasks and interactions difficult.
BROWSE
TRENDING
Insomnia Intestines Itch Listeria Lung Cancer Lung Damage Marijuana medical billing medication Menopause Mental Illness Music Obesity Odor Outbreak Pain Pain Medication Pasta pharma Prescription Drugs Psychoactive Rash Recall Recreational Drug Republicans RSV Sensitive Skin Skin Allergy Skincare sleep Sleep Apnea Smoking Snoring Stroke Sweat Tobacco Tomatoes treatment trend Trump Tylenol Vaccine Virus Weed Weight Loss
MAPS
LATEST
insert content here
USA
insert content here
WORLD
insert content here
FEATURED ARTICLES

Are There Any Safe Exercises for Seniors?
Discover safe and effective exercises designed specifically for seniors. Learn how low-impact cardio, gentle strength training, balance work, and daily stretching can help you stay...

10 Powerful Green Tea Benefits: Why This Ancient Drink Is Still a Modern Health Hero
1. Better Wellness Thanks To A Balanced Diet Of Antioxidants Green tea contains catechins, a type of oxidant that aids in protecting your cells from...

The Best Workouts for Older Adults: Stay Strong and Active at Any Age
Saying active isn’t just about fitness—it’s about independence, vitality, and confidence. Discover the best exercises for seniors that strengthen your body, protect your joints, and...

Can Prescription Treatments Prevent Acne Too?
If you’re visiting a dermatologist for acne, you might wonder whether prescription medications can also prevent future breakouts. Experts agree that most standard acne treatments...
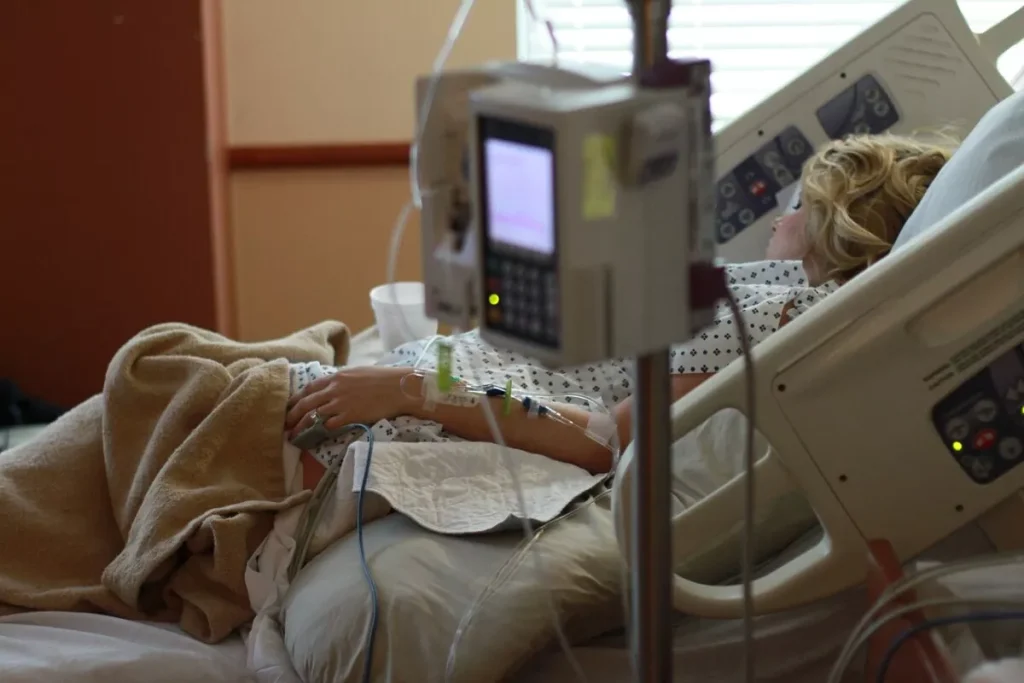
Hospitals Flooded with Patients Because of 3 Problems
According to a CNN report, hospitals across the country are reaching full capacity. The culprit is the tridemic between the Flu, RSV (respiratory syncytial virus),...

5 Steps to Reduce Alzheimer’s Disease
If you want to remain sharp and be in control of your life during your senior years, there are proactive techniques that will keep you...

3 Great Ways to Treat Skin Allergy
Many people believe that allergies solely have an effect on respiratory or digestive systems, but they can also affect your largest organ- your skin. As...
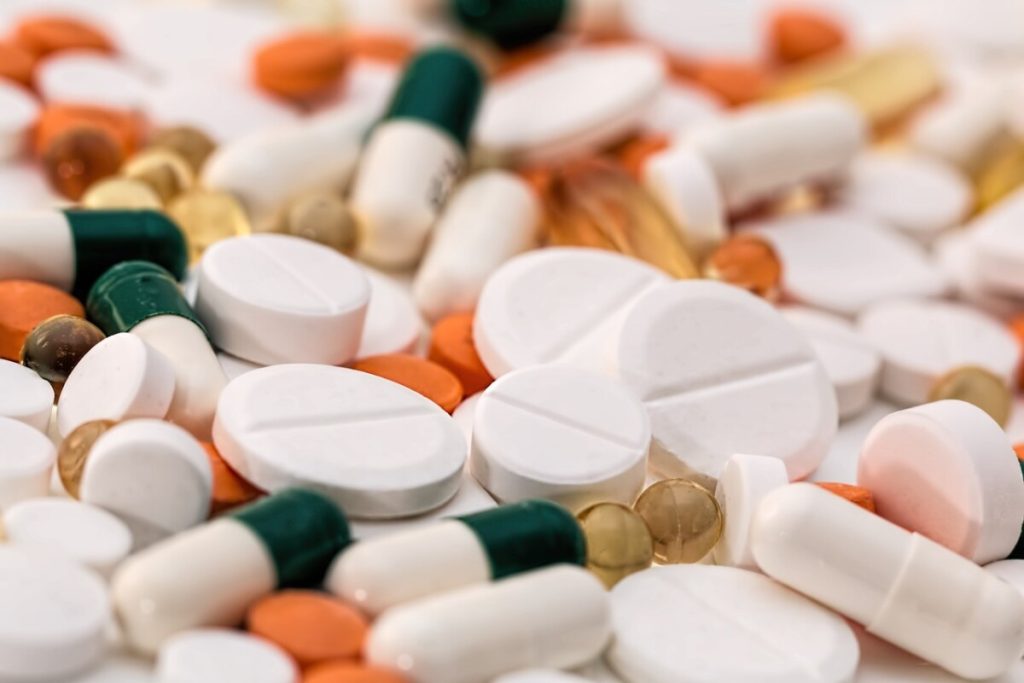
How Pain Medications Affect Your Guts
Pain medication is a type of medication that is used to relieve pain. It may be used for a wide range of several types of...

Putting a Stop to Bad Breath
Bad breath is a common problem that affects many people. It is often linked to poor dental hygiene, but there are other factors involved as...

Is Hypnotherapy Right for You?
Hypnosis has been around for thousands of years. From ancient Egypt to the present day, hypnosis has been used in religion, medicine, psychotherapy, and even...
{"arrow":"true","pagination":"true","speed":"1000","autoplay":"true","autoplay_speed":"15000","loop":"true","flex_animation":"slide","flex_slide_to_show":"5","flex_max_slide_to_show":"10","flex_slide_to_scroll":"1","flex_slide_margin":"0","flex_slide_width":"0","flex_start_slide":0,"flex_ticker_hover":"true","flex_height_auto":"false","show_thumbnail":"true","flex_random_start":"false","caption":false,"flex_slider_mode":"horizontal"}
{"animation_fancy":"","transition_fancy":"","fancy_box_loop":""}